Qubic Achieves Over 55 Million Transfers Per Second for Smart Contract Executions
Escrito por
Equipo Qubic
9 ago 2024

Introduction
Speed and efficiency are critical for the execution of smart contracts - self-executing agreements coded to automatically enforce the terms of a contract. Qubic has now broken its previous record of 40 million transfers per second, by achieving an astonishing rate of over 55 million smart contract executions per second. This milestone sets a new standard for what’s possible in its decentralised ecosystem.
But why is fast smart contract execution so important? There are several reasons:
Scalability: Handles more transactions simultaneously, crucial for growing blockchain applications.
Real-Time Applications: Ensures smooth, instant operations in DeFi, gaming, and supply chains.
User Experience: Reduces wait times, enhancing user satisfaction and retention.
Economic Efficiency: Lowers transaction costs by reducing computational resources needed.
Security: Minimizes the window for attacks like frontrunning, maintaining integrity.
Adoption and Innovation: Encourages the development of complex, innovative dApps, boosting overall blockchain adoption.
In this post, discover how we achieved 55 million transfers per second with our benchmarking exercise. We'll also present evidence to back up our claims—proving once again why Qubic is leading the way in smart contract technology.
Objective
The main goal of the benchmarking exercise was to measure the maximum transfer rate that the Qubic network can achieve for smart contract execution. To push the system to its limits, we initiated 1 million transfers using a new simple function on the Qubic Smart Contract called `qUtil`.
The Benchmarking Process
Launching Modified Nodes: We deployed nodes with specialised code modifications that enabled us to track the performance during this intense test.
Triggering 1 Million Transfers: Using the `qubic-cli` tool, we initiated 1 million transfers on the `qUtils` smart contract. This process was designed to test how efficiently the network could handle a massive volume of transfers.
Modified Code Used for Benchmarking
The additional code was crucial in accurately measuring the time it took to process all 1 million transfers, giving us a precise transfer rate. The process below simulates the process of conducting an airdrop via a smart contract.
Address Pool: Transfers were made between addresses sourced from a predefined pool (Figure 1).
Transfer Calculation: The amount of QUBIC to transfer was pseudo-randomly generated from the address pool and pre-calculated (Figure 2).
Transfer Rate Calculation: The transfer rate was calculated by dividing the total number of transfers by the time taken to process them (Figure 3). This helped us determine the system's efficiency under heavy load.

Figure 1: how addresses are sourced from the predefined address pool

Figure 2: how the amount of QUBIC to transfer is calculated

Figure 3: the transfer rate calculation process

Figure 3: the transfer rate calculation process (continued)
The Core Code
For those interested in the technical details, the core code used for this test can be found on GitHub.
Here is the Command to Run
qubic-cli:
https://github.com/qubic/qubic-cli/tree/cyber-pc-qutils-transfer-benchmark
Run command: ./qubic-cli -nodeip <ip> -nodeport <port> -seed <seed> -qutilsendtomanybenchmark 1000000
Results
The node successfully handled over 41 million transfers per second during the first test (Figure 4), indicating a highly efficient transfer rate and beating our previous record of 40 million transfers per second.
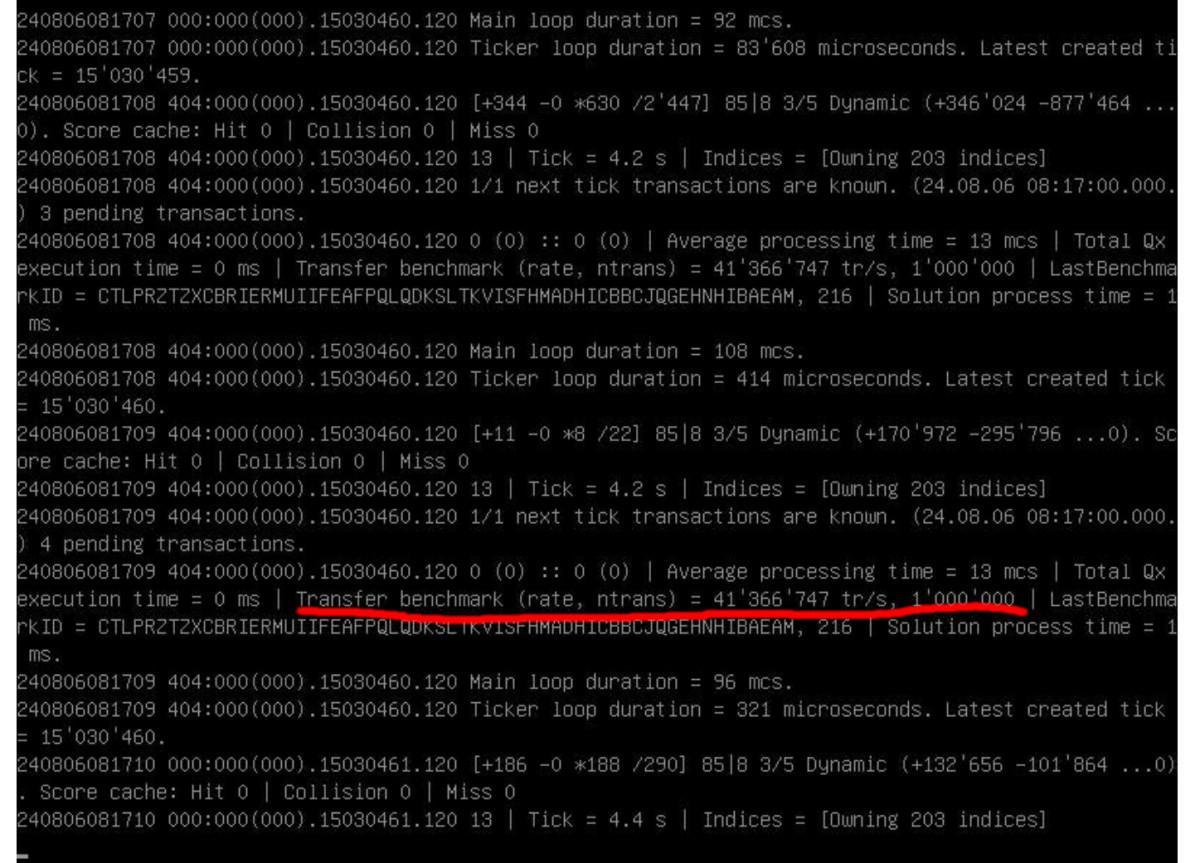
Figure 4: transfer rate showing 41,366,747 transfers per second
A second test again resulted in the node handling over 40 million transfers per second (Figure 5).

Figure 5: transfer rate showing 40,469,009 transfers per second
The third test was where the real breakthrough occurred, with the node achieving an incredible performance of over 55 million transfers per second! (See Figure 6).

Figure 6: Transfer rate showing 55,105,020 transfers per second
Successful Transfer Verification
We verified the success of these transfers by checking the balance and transaction logs of the last address involved (Figure 7). Everything matched perfectly, confirming the accuracy and reliability of the transfer process.
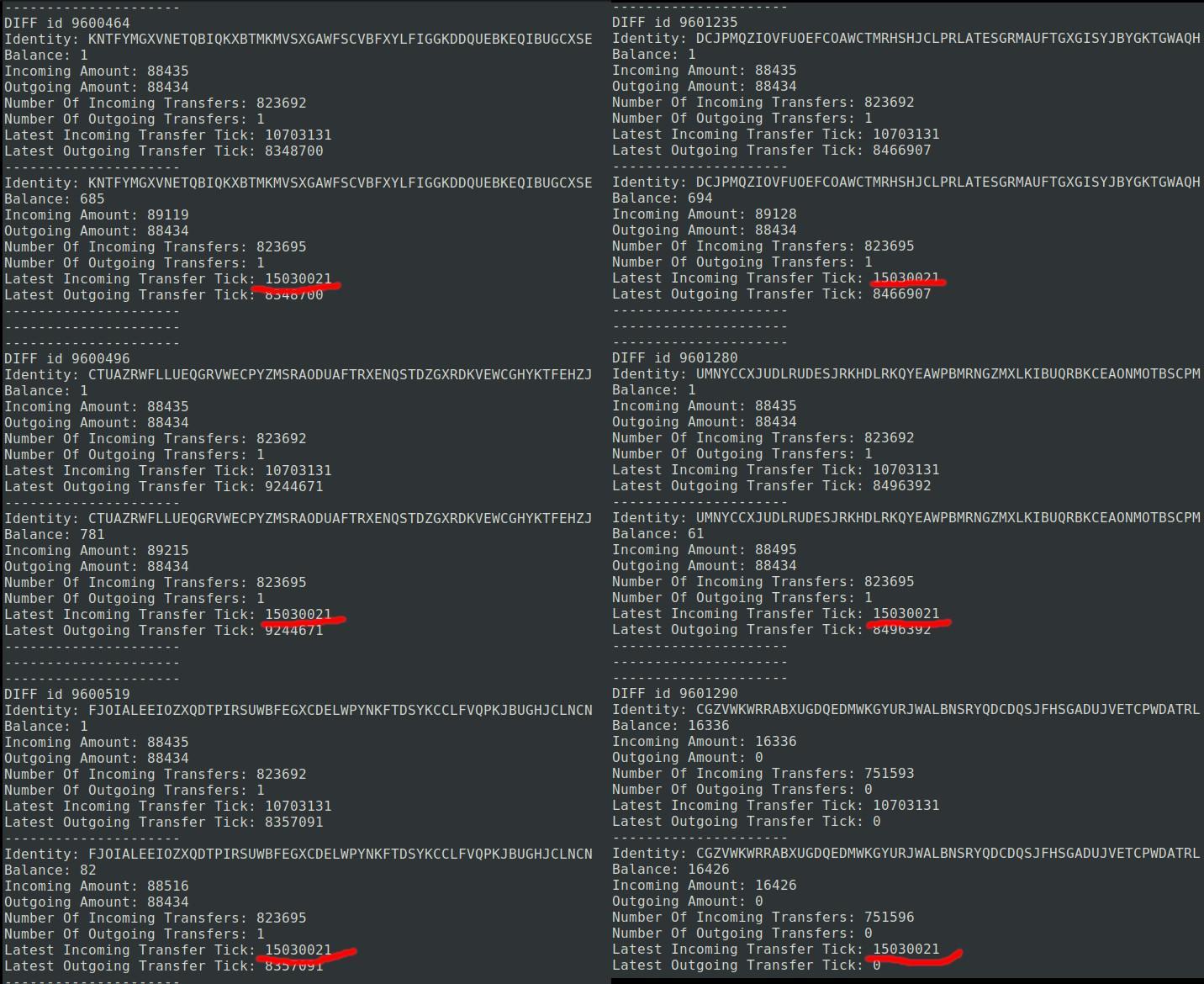
Figure 7: successful transfer verification
Spectrum File Changes
The maximum number of pool addresses (262,000) were fully utilised during the transfer operation (1 million transfers), and this usage is reflected in changes observed in a specific monitoring file (the spectrum file) (Figure 8).

Figure 8: the spectrum file changes
Conclusion
This benchmarking exercise proves that the Qubic network is capable of handling a vast number of transfers per second during smart contract execution. Achieving over 55 million transfers per second showcases the ecosystem's potential for large-scale operations.
Fast smart contract execution is vital for maintaining a scalable, user-friendly, secure, and economical ecosystem. It plays a critical role in the practical application and future widespread adoption of Qubic’s technology.
This performance highlights Qubic as a leader in smart contract technology, with the power to support even the most demanding applications.
We can’t wait to hear your thoughts on this. Join the discussion in Discord.
